The various methods of basement excavation are as follows:
Perimeter Trench Method: The perimeter trench method is used where weak soils are encountered; a trench wide enough to enable the retaining walls to be constructed is excavated around the perimeter of the site, and timbered according to the soil conditions. The permanent retaining walls are constructed within the trench excavation and the timbering is removed; the dumpling or middle can then be excavated and the base cast and joined to the retaining walls. This method could also be used in firm soils when the mechanical excavators required for bulk excavation are not available.
 |
| Figure 1. Perimeter Trench Method |
Ground Anchorage Method: Ground anchor is basically a pre-stressing tendon embedded and anchored into soil or rock to provide resistance to structural movements by a “tying back" principle.
Ground anchor can be classified into:
1. Rock anchor – for anchorage in rock
2. Injection anchor – suitable for most cohesive and non-cohesive soils
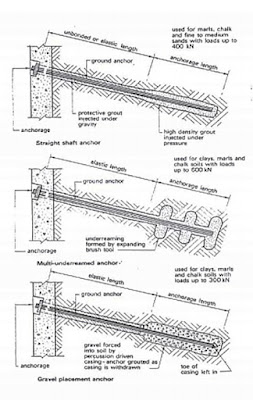 |
| Figure 2. Method to form Ground Anchor |
Method to form a ground anchor: A hole is predrilled on soil or rock in position carefully calculated. For rock anchor, an anchor bar with expanded sleeves at the end is inserted into the hole. A dense high strength grout is injected over a required length to develop sufficient resistance to hold the bar when it is stressed. Stressing is by hydraulic mean and when the stress is developed, the head of the bar is hold by an end plate and nut.
For injection anchor, a hole should be bored usually with an expanded end to increase anchorage ability. The pre-stressing bar is placed into the bore hole and pressure grouted over the anchorage length. Gravel placement ground anchor can also be used in clay soils for lighter loading. In this method irregular gravel is injected into the borehole over the anchorage length to form an end plug. The gravel plug is then force into soil using percussion method through casing, forming an enlarged end. A stressing bar is inserted into the casing and pressure grouted over the anchorage length as the casing is removed.
Reinforced Concrete Bored Piles: There are two main types of RC bored pile retaining wall:
i. Contiguous bored pile retaining wall
ii. Secant bored pile retaining wall
i. Contiguous bored pile retaining wall
ii. Secant bored pile retaining wall
 |
| Figure 3. Contiguous Bored Pile Wall |
Contiguous bored pile retaining wall: A contiguous bored pile is formed by constructing a series of individual vertical RC piles. The diameter of each pile in a contiguous piled wall is usually not less than 300 mm diameter. A small space usually of 100 mm is left in between adjacent piles. Once all the piles have been constructed the top of the piles are usually joined together by an RC capping beam. Contiguous piling is used in case of self-supporting soils such as stiff clays.
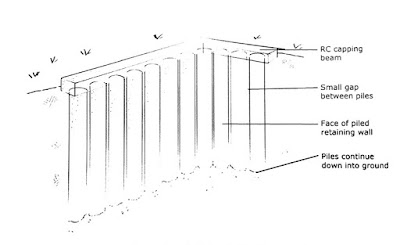 |
| Figure 4. Contiguous Bored Piled Wall with RC Capping Beam |
 |
| Figure 5. Basement Construction using Contiguous Bored Pile Wall |
Secant bored pile retaining wall: Secant bored pile walls are made using two types of piles: a soft unreinforced pile and a hard, strong reinforced concrete pile. The minimum diameter of each pile in a secant pile wall is usually 450 mm.
 |
| Figure 6. Secant Bored Pile Wall |
The construction sequence is:
(a) A line of unreinforced piles is constructed using low strength concrete. These are the soft piles.
(b) Then a second line of piles is constructed between and overlapping with the soft piles. The second line of piles is reinforced and uses high strength structural grade concrete. These are the hard piles.
The hard piles provide the structural strength. The soft piles act to fill the gap between the hard piles and hold back any ground or water that would otherwise be able to flow between the hard piles. Secant piling is used where the ground has a perceived risk of becoming fluid, commonly due to the combination of non-cohesive deposits and water. This technique will reduce the ground water ingress if designed and constructed correctly.
 |
| Figure 7. Steel Sheet Pile Wall |
Steel Sheet Piles: Sheet piled retaining walls are made by using interlocking steel piles. The steel sheet piles are generally driven or jacked into the ground using specialist plant. The plant is usually comparatively large which can be a limiting factor on their use. In addition head height clearance of at least the length of the sheet pile is required to allow installation. As a result steel sheet piles usually cannot be used underneath buildings. They are generally more suitable for open sites with good access as in the case of swimming pool.
Sheet piles are usually installed by either:
Percussive methods: hammering the sheet piles into the ground. This is generally not acceptable in urban areas due to excessive noise created by hammering.
Jacking: forcing the sheet piles into the ground using heavy hydraulic drivers.
Bonded Waterproofing Systems, LLC is the place to go for the best Interior Waterproofing, Foundation Repair, and Great Lakes Waterproofing in Greenwich, CT, and Bergenfield, NJ.
ReplyDeleteExcellent post! Very informative indeed. Thank you for sharing.
ReplyDelete- Excavation Rochester
This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteDiscover exciting nursing opportunities in England with our reputable healthcare team. We are hiring qualified nurses across specialties like medical, surgical, pediatric, and critical care. Candidates should hold a valid nursing license and relevant experience. We offer competitive salaries, comprehensive benefits, and professional development opportunities. Join a diverse, multidisciplinary team dedicated to outstanding patient care and high clinical standards. Make a significant impact on healthcare and advance your career with us. Apply today to become a valuable part of our mission to deliver exceptional healthcare services.
ReplyDeletehttps://www.dynamichealthstaff.com/nursing-jobs-in-england
"I found this post very informative and helpful. I've been considering using a Contiguous Wall for my new project, and this article provided valuable insights. I'm particularly interested in learning more about the benefits of contiguous walls in terms of energy efficiency and soundproofing. Thanks for sharing your expertise!"
ReplyDeleteHere's another option:
"Great article on contiguous walls! I've been researching different wall construction methods and this post has been very helpful. I'm curious to know if there are any specific considerations or challenges when using contiguous walls in seismic zones. Any advice would be appreciated."
The Uniaxial geogrid exporters in Ahmedabad is an excellent choice for soil reinforcement and stability. Designed for high tensile strength in one direction, the Uniaxial Geogrid enhances load distribution and prevents soil erosion, making it ideal for retaining walls and embankments. Its durable material ensures long-lasting performance even in harsh conditions. Easy to install and cost-effective, the Uniaxial Geogrid is a reliable solution for construction and civil engineering projects. Highly recommended for anyone needing superior ground reinforcement.
ReplyDeleteGreat post on basement excavation! Very useful for professionals at Bhagwati Machinery providing soil & rock anchoring service to ensure safety and stability in deep excavation projects. Thanks!
ReplyDelete